ABSTRACT:
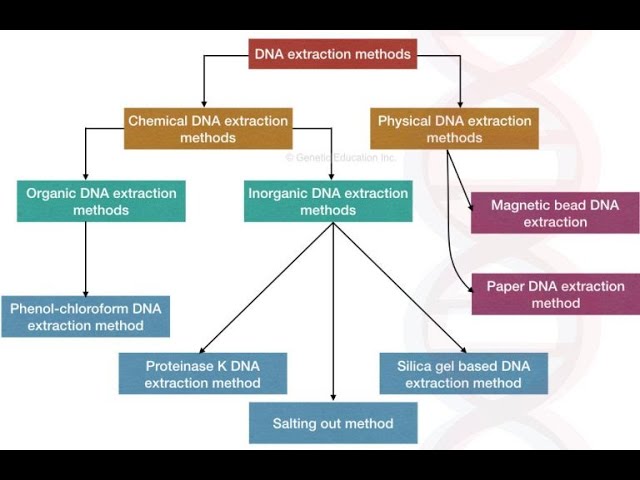
In this article, we will discuss about the fascinating methods of DNA extraction. DNA extraction is a method to purify DNA by using physical and/or chemical methods from a sample separating DNA from cell membranes, proteins, and other cellular components. Friedrich Miescher in 1869 did DNA isolation for the first time. There are different physical and chemical methods of DNA extraction. We will discuss here only chemical methods to extract DNA. We will also provide related references to understand the concept deeply.
INTRODUCTION OF METHODS OF DNA EXTRACTION:
DNA extraction is a fundamental step in molecular biology research, diagnostics, and forensic analysis. It involves isolating DNA from cells or tissues to study its structure, function, and genetic information. Over the years, various chemical methods have been developed to extract DNA efficiently and reliably. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the most commonly used chemical methods of DNA extraction, highlighting their principles, advantages, and limitations.
CHEMICAL METHODS OF DNA EXTRACTION:
1. PHENOL-CHLOROFORM DNA EXTRACTION:
Phenol-chloroform extraction is a classic method widely used for DNA extraction. It involves the use of phenol and chloroform, which separate DNA from other cellular components based on their differential solubility. Phenol denatures proteins, while chloroform extracts lipids, leaving DNA in the aqueous phase. This method is effective in removing contaminants, but it requires careful handling due to the toxicity of phenol and chloroform.

2. SALTING OUT METHOD OF DNA EXTRACTION:
The salting-out method is a simple and cost-effective DNA extraction technique. It utilizes high salt concentrations to precipitate proteins and other contaminants, leaving DNA in the supernatant. Ammonium acetate or sodium acetate commonly used as the salt. This method is suitable for extracting DNA from various sources, including blood, tissues, and bacteria. However, it may yield lower DNA purity compared to other methods.
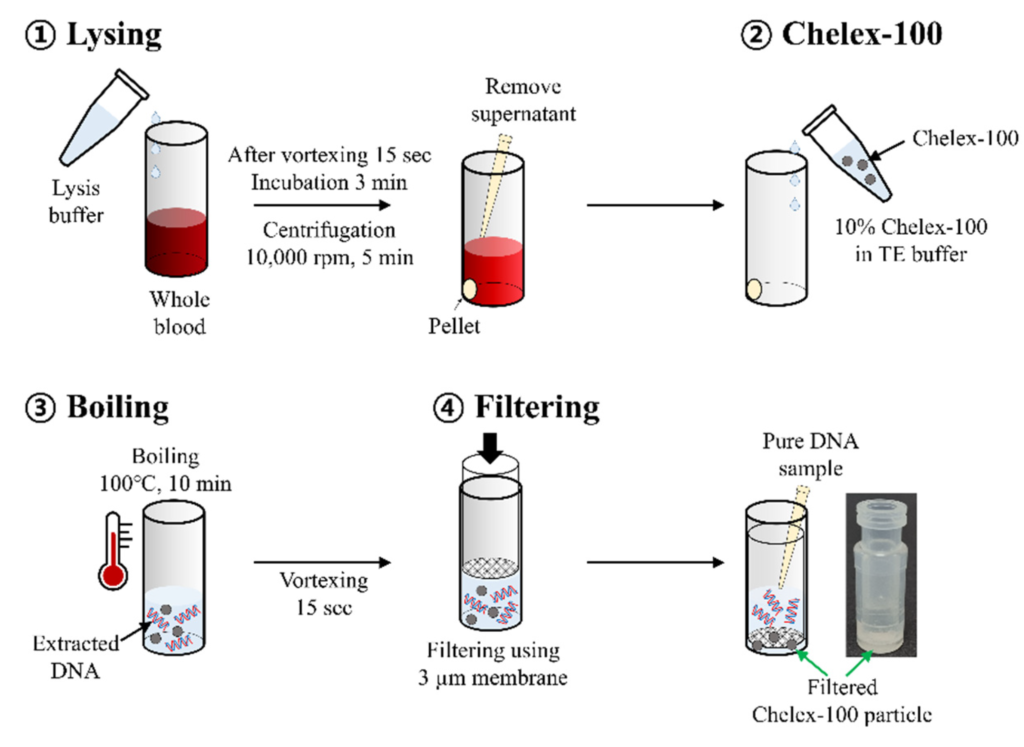
3. CHELEX EXTRACTION OF DNA:
Chelex extraction is a rapid and inexpensive method for DNA extraction. It utilizes a chelating resin called Chelex, which binds divalent metal ions required for DNA degradation. By removing these ions, Chelex prevents DNA degradation and facilitates its extraction. This method is particularly useful for PCR-based applications, as it provides high-quality DNA suitable for amplification. However, it may not be suitable for samples containing high levels of contaminants or inhibitors.
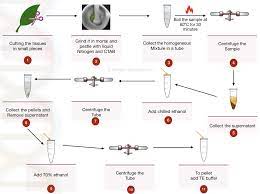
4. CTAB METHOD OF DNA EXTRACTION:
The CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide) method commonly used for DNA extraction from plant tissues. CTAB is a cationic detergent that selectively precipitates DNA by forming complexes with negatively charged cellular components. This method effectively removes polysaccharides, proteins, and other contaminants, resulting in high-quality DNA. However, it requires additional steps, such as chloroform extraction, to remove residual contaminants.
5. SILICA GEL BASED DNA EXTRACTION METHOD:
The silica gel-based method of DNA extraction a technique used to isolate DNA from various sources, such as cells, tissues, or biological fluids. It involves the binding of DNA to a silica gel matrix, followed by washing steps to remove impurities and elution of the purified DNA. The process begins with the lysis of the sample, which involves breaking down the cell or tissue structure to release the DNA. After lysis, the lysate mixed with a binding buffer that contains chaotropic salts, such as guanidine thiocyanate or guanidine hydrochloride.
The lysate and binding buffer mixture is then applied to a silica gel membrane or column, where the DNA binds to the silica gel matrix. Once the DNA is bound to the silica gel, other impurities, such as proteins, lipids, and cellular debris, are washed away using wash buffers with increasing concentrations of ethanol or isopropanol. Finally, the purified DNA is eluted from the silica gel matrix using a low-salt elution buffer or water. The elution buffer disrupts the interaction between DNA and silica gel, allowing the DNA to be released into the solution.

CONCLUSION:
Chemical methods of DNA extraction play a crucial role in various fields of research and diagnostics. Each method has its advantages and limitations, and the choice of method depends on the sample type, desired DNA quality, and available resources. Researchers should carefully consider these factors when selecting a DNA extraction method to ensure accurate and reliable results.
REFERENCES:
Sambrook, J., & Russell, D. W. (2001). Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. https://www.cshlpress.com/pdf/sample/2013/MC4/MC4FM.pdf
Boom, R., Sol, C. J., Salimans, M. M., Jansen, C. L., Wertheim-van Dillen, P. M., & van der Noordaa, J. (1990). Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. Journal of clinical microbiology, 28(3), 495-503. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1691208/
Walsh, P. S., Metzger, D. A., & Higuchi, R. (1991). Chelex 100 as a medium for simple extraction of DNA for PCR-based typing from forensic material. BioTechniques, 10(4), 506-513. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1867860/
Doyle, J. J., & Doyle, J. L. (1987). A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochemical Bulletin, 19(1), 11-15.


