ABSTRACT:
In this article, we will discuss about the the gastric diseases. These are the diseases related to the stomach and intestines. There are several causes of these diseases like over-eating, smoking, alcohol drinking, etc. We will discuss here about the causes, symptoms, effects and treatments of the diseases related to stomach and intestines. We will also provide references to acknowledge and learn about the gastro-intestinal diseases.
INTRODUCTION OF GASTRIC DISEASES:
A broad spectrum of disorders that affect stomach and cause pain, discomfort, and even life-threatening consequences referred to as gastric illnesses. It is essential to comprehend various disorders, ranging from minor ailments like gastritis to serious problems like stomach cancer, in order to treat them early on. An overview of the many kinds of stomach illnesses, together with information on their causes, symptoms, and treatments, given in this article.
TYPES OF GASTRIC DISEASES:
1. GASTRITIS:
Gastritis is the term for either acute or persistent stomach lining irritation. Abdominal discomfort, nausea, vomiting, bloating, and appetite loss are typical symptoms. Irritating substances like alcohol, medicines (such nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), and bacterial infections (like Helicobacter pylori) are common causes of acute gastritis. Prolonged inflammation, autoimmune diseases, or H. pylori infection can all lead to chronic gastritis. Antibiotics for bacterial infections, lifestyle changes, and drugs to lower stomach acid are commonly used in treatment.
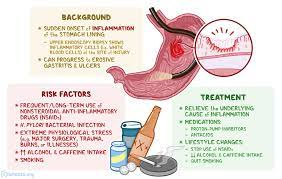
2. PEPTIC ULCERS:
Sores on the lining of the stomach, small intestine, or esophagus are known as peptic ulcers. Bloating, nausea, vomiting, and searing pain in the belly can all be symptoms of these ulcers. Long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications and Helicobacter pylori infection are major causes. Antibiotics to kill H. pylori, drugs to lessen the production of stomach acid, and lifestyle modifications are all part of the treatment.

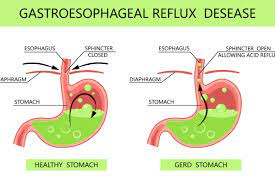
3. GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE:
Heartburn, regurgitation, chest discomfort, and trouble swallowing are among the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which is caused by stomach acid flowing back into the esophagus. Obesity, pregnancy, hiatal hernias, and certain diets are risk factors. Treatment options include diet and lifestyle adjustments (such as losing weight), drugs to suppress acid production, and, in extreme situations, surgery to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter.
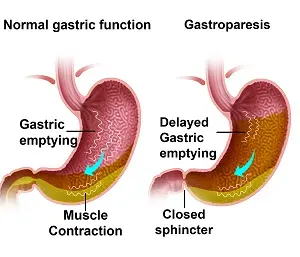
4. GASTROPARESIS:
Delayed stomach emptying, resulting in symptoms including nausea, vomiting, bloating, and early satiety, is the hallmark of gastroparesis. Common reasons include neurological conditions, diabetes, and stomach surgery. The mainstay of treatment is symptom control, which may involve small, frequent meals, medicines to promote stomach emptying, or, in extreme situations, surgery.
5. GASTRIC CANCER- ACUTE TYPE OF GASTRIC DISEASES:
A malignant growth that forms in the stomach lining is called gastric cancer. The symptoms, which can include blood in the stool, trouble swallowing, vomiting, unexpected weight loss, and stomach discomfort, frequently appear in severe stages. A family history of stomach cancer, smoking, obesity, and H. pylori infection are risk factors. Depending on the cancer’s stage and extent, treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy.
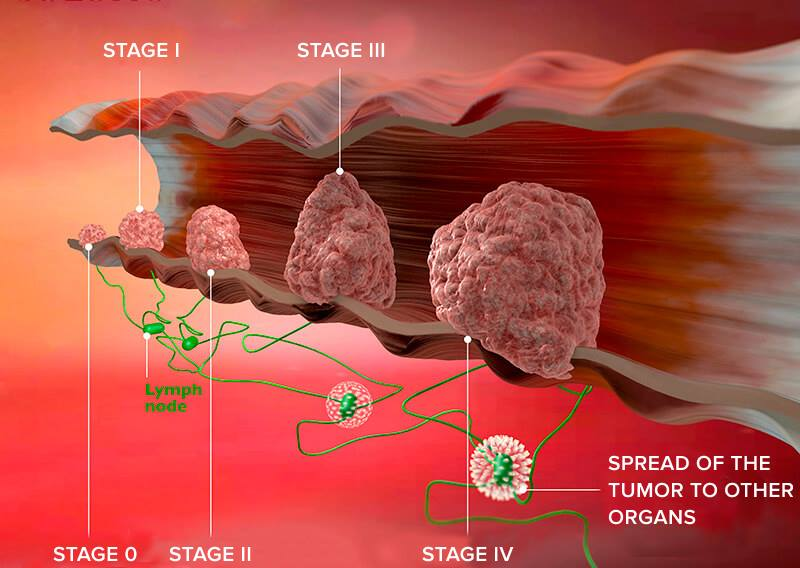
6. GASTROINTESTINAL STROMAL TUMOR:
Rare tumors known as GISTs can develop in the stomach or other digestive tract regions. Abdominal discomfort, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and blood in the stool are possible symptoms. Although the precise reason is frequently unclear, genetic alterations have been linked to certain instances. Tumor excision surgery, targeted therapy, chemotherapy, and occasionally radiation therapy are all part of the treatment plan.

CONCLUSION-GASTRIC DISEASES:
There is a wide variety of disorders under the umbrella of gastric diseases, each with unique symptoms, etiology, and therapeutic modalities. Improving results and avoiding problems need early detection and treatment. For an accurate diagnosis and course of treatment, get medical help as soon as possible if your gastrointestinal problems are bothersome.
REFERENCES:
Malfertheiner, P., Megraud, F., O’Morain, C. A., et al. (2017). Management of Helicobacter pylori infection—the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut, 66(1), 6-30. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27707777/
Rubenstein, J. H., & Taylor, J. B. (2019). Meta-analysis: the association of oesophageal adenocarcinoma with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 40(8), 842-854. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20955441/
Strong, V. E. (2019). Progress in gastric cancer. Updates in Surgery, 71(2), 213-217. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7680370/
Van Cutsem, E., Cervantes, A., Adam, R., et al. (2016). ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Annals of Oncology, 27(8), 1386-1422. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27380959/