ABSTRACT:
In this article, we will discuss about the sexually transmitted diseases. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), sometimes referred to as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), are a major global health concern that impact millions of individuals annually. All forms of sexual intercourse, including oral, anal, and vaginal sex, can transmit these illnesses. While there are STDs that are easily treatable and curable, there are others that, if neglected, can have serious negative effects on health. We will also provide references to learn and acknowledge the concept of STDs.
INTRODUCTION OF SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES:
Infections contracted through sexual contact known as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) or sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Regardless of age, gender, or sexual orientation, they can impact anyone who engages in sexual activity. Promoting sexual health and well-being requires an understanding of STDs, their risks, preventative strategies, and accessible therapies.
TYPES OF SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES:
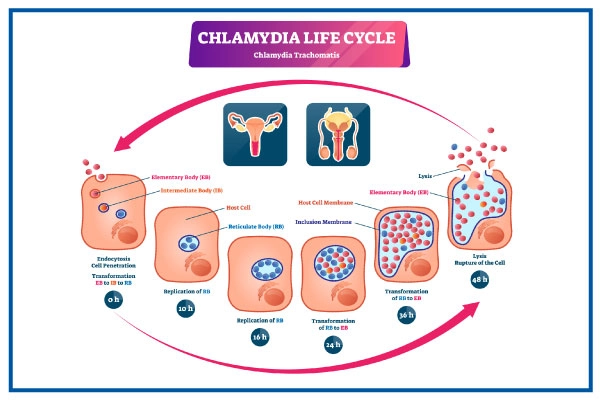
1. CHLAMYDIA:
It can cause major health and reproductive problems if left untreated. It caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis and can infect the genital tract.
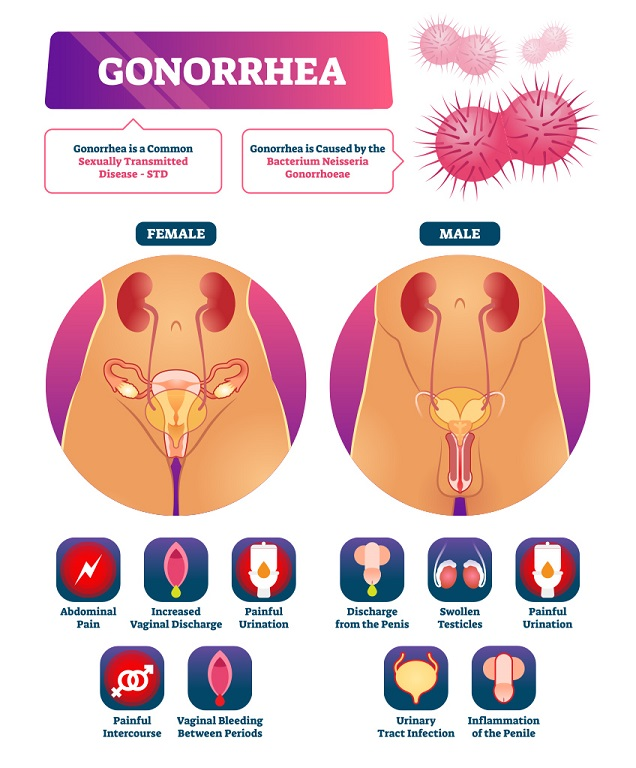
2. GONORRHEA:
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, the bacterium that causes it, can infect the throat, rectum, and genital tract. If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to infertility and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
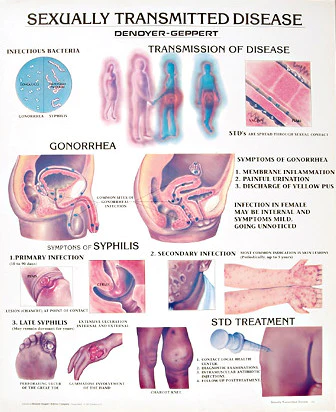
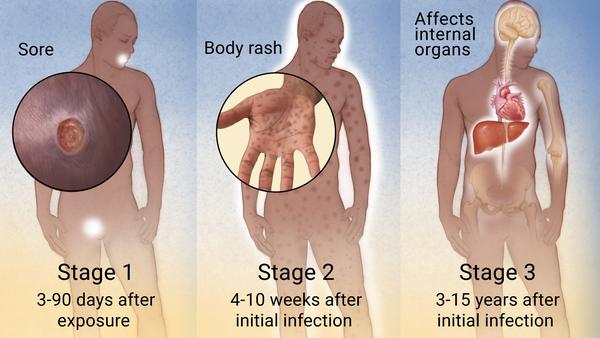
3. SYPHILIS:
Syphilis, which brought on by the bacteria Treponema pallidum, develops gradually and, if left untreated, can have serious side effects that include harm to the liver, blood vessels, brain, eyes, nerves, bones, and joints.
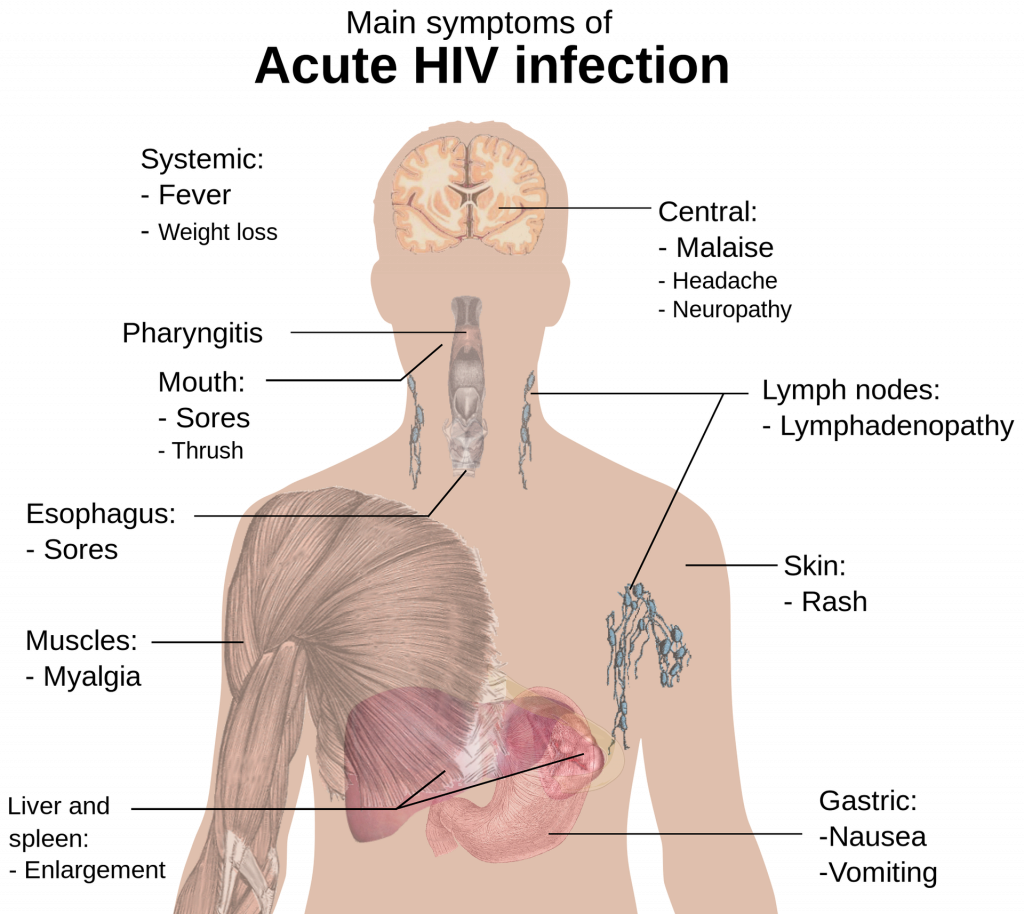
4. HUMAN IMMUNODEFICIENCY VIRUS:
HIV especially targets CD4 cells (T cells), which are essential for assisting the body in fending off infections, as part of its attack on the immune system. HIV can develop into acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) if treatment is not received.
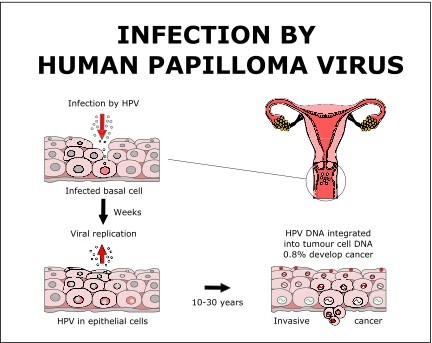
5. HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS:
The most prevalent sexually transmitted infection is HPV. Certain strains can result in warts on the genitalia, while other strains can develop malignancies of the throat, anal, or cervical regions.
6. HERPES:
Herpes is a highly contagious condition that can result in painful vaginal sores and is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV).
CAUSES OF SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES:
1. BACTERIAL INFECTIONS:
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) like gonorrhea, syphilis, and chlamydia are brought on by germs and can be contracted through unprotected sexual contact with an infected person.
2. VIRAL INFECTIONS:
Human papillomavirus (HPV), herpes simplex virus (HSV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and hepatitis B and C viruses are examples of viral STDs that are spread through sexual activity or contact with infected bodily fluids.
3. PARASITIC INFECTIONS:
Sexual contact with an infected person can result in the transmission of parasitic sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), such as trichomoniasis.
4. UNPROTECTED SEX AND OTHER ACTIVITIES:
The risk of catching an STD rises when having unprotected intercourse, such as vaginal, anal, or oral sex without the use of condoms or other barrier techniques. The risk of contracting sexually transmitted infections (STDs) is increased when one has several relationships or interacts sexually with those who have multiple partners. Abuse of substances, such as drugs and alcohol, can cause poor judgment and unsafe sexual conduct, which raises the chance of getting STIs. Inadequate availability of sexual health services, such as testing, treatment, and education, may be a factor in the transmission of STDs among populations.
EFFECTS OF SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES:
Untreated sexually transmitted infections (STDs) can result in a variety of physical health issues, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), infertility, persistent discomfort, genital warts, genital sores, and some cancers (such as HPV-related cervical cancer). Through ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, infertility, and unfavorable pregnancy and delivery outcomes, STDs can have an impact on reproductive health. Some sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can raise one’s chance of contracting or spreading HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, including genital herpes, syphilis, and chancroid. Receiving an STD diagnosis can have negative psychological and emotional effects, such as social stigma and difficulties in sexual relationships. It can also cause emotions of guilt, humiliation, worry, and melancholy.
PREVENTIONS AND TREATMENTS OF STDs:
Prevention is key in reducing the spread of STDs. Effective preventive measures include: the best defense against sexually transmitted infections is abstinence from sexual activity. The chance of getting an STD can be considerably decreased by using condoms correctly and consistently. A mutually monogamous sexual relationship with a partner who is not affected can reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections. There are vaccines available to prevent against infection against several STDs, such as hepatitis B and HPV. Regular STD testing can aid in the early detection of infections and the prevention of their transmission, particularly for those who are sexually active or participate in high-risk behaviors.
Treatment for sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) varies according on the type of infection, but it may involve: Antibiotics for bacterial infections such as syphilis, gonorrhea, and chlamydia. antiviral drugs for herpes and HIV-related illnesses. drugs for the treatment of problems and symptoms.
routine observation and post-treatment care.
CONCLUSION-SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES:
The well-being of society, the general public, and individual health are all seriously threatened by sexually transmitted diseases. In order to lower the prevalence and effect of STDs, preventive measures are crucial. These include consistent and proper condom use, routine testing and screening, vaccination (such as the HPV vaccine), limiting the number of sexual partners, and abstaining from risky sexual activity. In addition, addressing the underlying causes of STD transmission and advancing sexual health and wellbeing for all depend heavily on expanding access to comprehensive sexual health care, information, and resources.
REFERENCES:
World Health Organization. (2021). Sexually transmitted infections (STIs). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/sexually-transmitted-infections-(stis)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020). Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs). https://www.cdc.gov/std/default.htm
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). https://www.cdc.gov/std/default.htm



